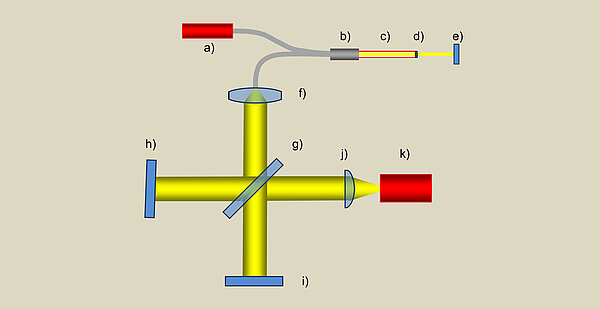
Distance sensors based on the interferometer principle measure the transit time difference between two light beams (measurement beam and reference beam), which results from the difference in length between a reference distance (distance to the reference surface) and the measurement distance (distance to the measurement object surface) (Fig. 8). The evaluation is carried out by determining the phase shift when the two beams are superimposed. By simultaneously using several slightly different frequencies (colours), the absolute value of the distance to the object surface can be measured from the resulting beat (heterodyne method).
- Development
-
Machines
- Coordinate measuring machines with X-Y table
- Coordinate measuring machines with guideways in a single plane
- Coordinate measuring machines with bridge
- Coordinate measuring machines with rotary axes
- Coordinate measuring machines for two-dimensional measurements
- Coordinate measuring machines with X-ray tomography
- Coordinate measuring machines for special applications
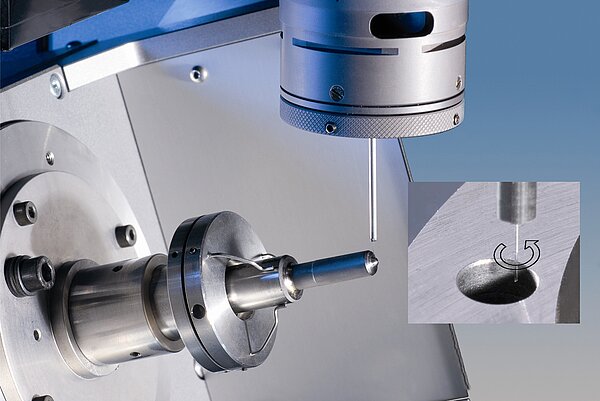
- Sensors
- Software
- Special characteristics
- Accuracy
- Publications
- Literature page